Bài tập cuối chương 5 trang 33 Vở bài tập toán lớp 6 tập 2 NXB Chân Trời Sáng Tạo
\(1\). Sắp xếp các số sau theo thứ tự tăng dần: \(\displaystyle \frac 2{5}{7}; \displaystyle \frac {-5}{8}; \displaystyle \frac {7}{-9}; \displaystyle \frac {13}{5}.\)
Giải
Ta có:
\(2\displaystyle \frac {5}{7}=\displaystyle \frac {19}{7}=\displaystyle \frac {95}{35}; \displaystyle \frac {13}{5}=\displaystyle \frac {91}{35}.\)
\(\displaystyle \frac {-5}{8}=\displaystyle \frac {-45}{72}; \displaystyle \frac {7}{-9}=\displaystyle \frac {-56}{72}.\)
Vì \(\displaystyle \frac {-56}{72}<\displaystyle \frac {-45}{72}<\displaystyle \frac {91}{35}<\displaystyle \frac {95}{25}\)
nên ta suy ra thứ tự cần tìm là: \(\displaystyle \frac {7}{-9};\displaystyle \frac {-5}{8};\displaystyle \frac {13}{5};2\displaystyle \frac {5}{7}.\)
\(\)
\(2\). Tính giá trị biểu thức \(A=\displaystyle \frac {-3}{2}.\displaystyle \frac {m}{n}+\displaystyle \frac {3}{-8}.2\displaystyle \frac {1}{2}\) khi \(\displaystyle \frac {m}{n}\) nhận các giá trị:
a) \(\displaystyle \frac {4}{5};\)
b) \(\displaystyle \frac {-3}{8};\)
c) \(\displaystyle \frac {0}{-2021};\)
d) \(\displaystyle \frac {5}{2}.\)
Giải
a)
\(A=\displaystyle \frac {-3}{2}.\displaystyle \frac {4}{5}+\displaystyle \frac {3}{-8}.2\displaystyle \frac {1}{2}=\displaystyle \frac {-6}{5}+\displaystyle \frac {3}{-8}.\displaystyle \frac {5}{2}\)
\(=\displaystyle \frac {-6}{5}+\displaystyle \frac {-15}{16}=\displaystyle \frac {-96}{80}+\displaystyle \frac {-75}{80}=\displaystyle \frac {-171}{80}.\)
b)
\(A=\displaystyle \frac {-3}{2}.\displaystyle \frac {-3}{8}+\displaystyle \frac {3}{-8}.2\displaystyle \frac {1}{2}=\displaystyle \frac {9}{16}+\displaystyle \frac {3}{-8}.\displaystyle \frac {5}{2}\)
\(=\displaystyle \frac {9}{16}+\displaystyle \frac {-15}{16}=\displaystyle \frac {-6}{16}=\displaystyle \frac {-3}{8}.\)
c)
\(A=\displaystyle \frac {-3}{2}.0+\displaystyle \frac {3}{-8}.2\displaystyle \frac {1}{2}=\displaystyle \frac {3}{-8}.\displaystyle \frac {5}{2}=\displaystyle \frac {-15}{16}.\)
d)
\(A=\displaystyle \frac {-3}{2}.\displaystyle \frac {5}{2}+\displaystyle \frac {3}{-8}.2\displaystyle \frac {1}{2}=\displaystyle \frac {-15}{4}+\displaystyle \frac {3}{-8}.\displaystyle \frac {5}{2}\)
\(=\displaystyle \frac {-15}{4}+\displaystyle \frac {-15}{16}=\displaystyle \frac {-60}{16}+\displaystyle \frac {-15}{16}=\displaystyle \frac {-75}{16}.\)
\(\)
\(3\). Hoàn thành bảng trừ và bảng chia sau đây:
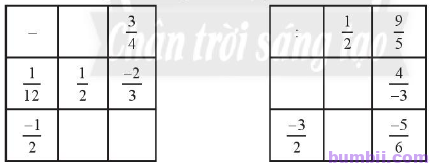
Giải
Bảng trừ:
Ta có:
\(\displaystyle \frac {1}{12}-x=\displaystyle \frac {1}{2} \Rightarrow x=\displaystyle \frac {1}{12}-\displaystyle \frac {1}{2}\)
\(\Rightarrow x=\displaystyle \frac {1}{12}-\displaystyle \frac {6}{12} \Rightarrow x=\displaystyle \frac {-5}{12}.\)
\(\displaystyle \frac {-1}{2}-x=\displaystyle \frac {-1}{2}-\displaystyle \frac {-5}{12}=\displaystyle \frac {-6}{12}-\displaystyle \frac {-5}{12}=\displaystyle \frac {-1}{12}.\)
\(\displaystyle \frac {-1}{2}-\displaystyle \frac {3}{4}=\displaystyle \frac {-2}{4}-\displaystyle \frac {3}{4}=\displaystyle \frac {-5}{4}.\)
Bảng chia:
Ta có:
\(x \div \displaystyle \frac {9}{5}=\displaystyle \frac {4}{-3} \Rightarrow x=\displaystyle \frac {4}{-3}.\displaystyle \frac {9}{5} \Rightarrow x=\displaystyle \frac {-12}{5}.\)
\(x \div \displaystyle \frac {1}{2}=\displaystyle \frac {-12}{5} \div \displaystyle \frac {1}{2}=\displaystyle \frac {-12}{5}.\displaystyle \frac {2}{1}=\displaystyle \frac {-24}{5}.\)
\(\displaystyle \frac {-3}{2} \div \displaystyle \frac {1}{2}=\displaystyle \frac {-3}{2}.\displaystyle \frac {2}{1}=-3.\)
\(\)
\(4\). Tìm \(x,\) biết:
a) \(\displaystyle \frac {7}{-8}-x=\displaystyle \frac {-4}{5}:\displaystyle \frac {3}{10};\)
b) \(\displaystyle \frac {-5}{6}.x=\displaystyle \frac {-5}{8}-1\displaystyle \frac {3}{4}.\)
Giải
a)
\(\displaystyle \frac {7}{-8}-x=\displaystyle \frac {-4}{5}:\displaystyle \frac {3}{10} \Rightarrow \displaystyle \frac {7}{-8}-x=\displaystyle \frac {-4}{5}.\displaystyle \frac {10}{3}\)
\(\Rightarrow \displaystyle \frac {7}{-8}-x=\displaystyle \frac {-40}{15} \Rightarrow x=\displaystyle \frac {7}{-8}-\displaystyle \frac {-40}{15}\)
\(\Rightarrow x=\displaystyle \frac {-105}{120}-\displaystyle \frac {-320}{120} \Rightarrow x=\displaystyle \frac {215}{120} \Rightarrow x=\displaystyle \frac {43}{24}.\)
b)
\(\displaystyle \frac {-5}{6}.x=\displaystyle \frac {-5}{8}-1\displaystyle \frac {3}{4} \Rightarrow \displaystyle \frac {-5}{6}.x=\displaystyle \frac {-5}{8}-\displaystyle \frac {7}{4}\)
\(\Rightarrow \displaystyle \frac {-5}{6}.x=\displaystyle \frac {-5}{8}-\displaystyle \frac {14}{8} \Rightarrow \displaystyle \frac {-5}{6}.x=\displaystyle \frac {-19}{8}\)
\(\Rightarrow x=\displaystyle \frac {-19}{8} \div \displaystyle \frac {-5}{6} \Rightarrow x=\displaystyle \frac {-19}{8}.\displaystyle \frac {6}{-5}\)
\(\Rightarrow x=\displaystyle \frac {114}{40} \Rightarrow x=\displaystyle \frac {57}{20}.\)
\(\)
\(5\). Một lớp học có số học sinh nam bằng \(\displaystyle \frac {2}{3}\) số học sinh nữ. Hỏi số học sinh nam bằng bao nhiêu phần số học sinh cả lớp?
Giải
Theo đề bài, nếu chia số học sinh nữ thành \(3\) phần bằng nhau thì số học sinh nam sẽ chiếm \(2\) phần.
Lớp gồm học sinh nam và học sinh nữ nên sẽ có tổng cộng là \(2+3=5\) (phần).
Vậy số học sinh nam bằng \(\displaystyle \frac {2}{5}\) số học sinh cả lớp.
\(\)
\(6\). Ba cửa hàng bán lẻ hoa quả nhập tổng cộng \(48 \text{ } kg\) cam của một nhà vườn để bán lẻ cho người tiêu dùng. Cửa hàng thứ nhất nhập \(\displaystyle \frac {3}{8}\) khối lượng. Cửa hàng thứ hai nhập \(\displaystyle \frac {2}{5}\) khối lượng còn lại và \(2 \text{ } kg.\) Hỏi cửa hàng thứ ba nhập bao nhiêu ki-lô-gam?
Giải
Cửa hàng thứ nhất nhập:
\(\displaystyle \frac {3}{8}.48=18 \text{ } (kg)\)
Cửa hàng thứ hai nhập:
\(\displaystyle \frac {2}{5}.(48-18)+2=\displaystyle \frac {2}{5}.30+2=14 \text{ } (kg)\)
Cửa hàng thứ ba nhập:
\(48-18-14=16 \text{ } (kg)\)
\(\)
\(7\). Khối \(6\) của một trường học có ba lớp \(6\). Lớp \(6A\) có số học sinh bằng \(\displaystyle \frac {6}{11}\) số học sinh hai lớp còn lại. Lớp \(6C\) có số học sinh bằng \(\displaystyle \frac {1}{2}\) số học sinh hai lớp còn lại. Số học sinh lớp \(6B\) là \(32.\) Tính số học sinh khối \(6\) của trường.
Giải
Lập luận tương tự bài số \(5\), ta suy ra:
Số học sinh lớp \(6A, 6C\) lần lượt chiếm \(\displaystyle \frac {6}{17}, \displaystyle \frac {1}{3}\) số học sinh của khối \(6.\)
Suy ra số học sinh của lớp \(6B\) chiếm \(1-\displaystyle \frac {6}{17}-\displaystyle \frac {1}{3}\) số học sinh của khối \(6.\)
Gọi \(x\) là số học sinh của khối \(6\), ta có:
\(\left(1-\displaystyle \frac {6}{17}-\displaystyle \frac {1}{3}\right).x=32 \Rightarrow \left(1-\displaystyle \frac {18}{51}-\displaystyle \frac {17}{51}\right).x=32\)
\(\Rightarrow \left(1-\displaystyle \frac {35}{51}\right).x=32 \Rightarrow \displaystyle \frac {16}{51}.x=32\)
\(\Rightarrow x = 32 \div\displaystyle \frac {16}{51} \Rightarrow x = 32.\displaystyle \frac {51}{16} \Rightarrow x=102.\)
Vậy khối \(6\) có \(102\) học sinh.
\(\)
\(8\). Theo số liệu của Bộ Công Thương, \(8\) tháng đầu năm \(2020\) Việt Nam xuất khẩu được khoảng \(\displaystyle \frac {9}{2}\) triệu tấn gạo với tổng giá trị \(251\) triệu USD. So sánh thấy, khối lượng này bằng \(\displaystyle \frac {983}{1000}\) khối lượng cùng kì \(8\) tháng đầu năm \(2019\) và giá trị tính theo USD bằng \(\displaystyle \frac {1104}{1000}\) giá trị cùng kì \(8\) tháng đầu năm \(2019.\) Tìm phân số biểu thị chênh lệch giữa khối lượng gạo xuất khẩu trong \(8\) tháng đầu năm \(2020\) so với cùng kì năm \(2019\) và số chênh lệch giữa hai giá trị tính theo USD tương ứng.
Giải
Khối lượng gạo xuất khẩu trong \(8\) tháng đầu năm \(2019\) là:
\(\displaystyle \frac {9}{2}\div\displaystyle \frac {983}{1000}=\displaystyle \frac {9}{2}.\displaystyle \frac {1000}{983}=\displaystyle \frac {4500}{983}\) (triệu tấn)
Chênh lệch giữa khối lượng gạo xuất khẩu trong \(8\) tháng đầu năm \(2020\) so với cùng kì năm \(2019\) là:
\(\displaystyle \frac {9}{2}-\displaystyle \frac {4500}{983}=\displaystyle \frac {-153}{1966}\) (triệu tấn)
Giá trị gạo xuất khẩu trong \(8\) tháng đầu năm \(2019\) là:
\(251\div\displaystyle \frac {1104}{1000}=251.\displaystyle \frac {1000}{1104}=\displaystyle \frac {31375}{138}\) (triệu USD)
Chênh lệch giữa giá trị gạo xuất khẩu trong \(8\) tháng đầu năm \(2020\) so với cùng kì năm \(2019\) là:
\(251-\displaystyle \frac {31375}{138}=\displaystyle \frac {3263}{138}\) (triệu USD)
Vậy khối lượng giảm \(\displaystyle \frac {153}{1966}\) triệu tấn và giá trị tăng \(\displaystyle \frac {3263}{138}\) triệu USD.
\(\)
Xem bài giải trước: Bài 7. Hỗn số
Xem bài giải tiếp theo:
Xem các bài giải khác: Giải bài tập Toán Lớp 6 – NXB Chân Trời Sáng Tạo

Đường tuy ngắn không đi không đến; Việc tuy nhỏ không làm không nên.